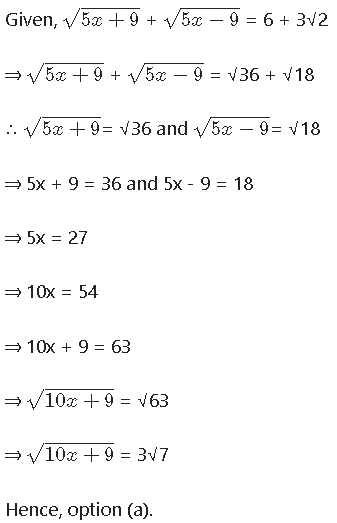Live Updates
• CATKing has launched new chat bot.

• New video on Logs has been released.
13.2K
Learners
asked the doubt

Previous Year Questions
The schematic diagram below shows 12 rectangular houses in a housing complex. House numbers are mentioned in the rectangles representing the houses. The houses are located in six columns – Column-A through Column-F, and two rows – Row-1 and Row-2. The houses are divided into two blocks - Block XX and Block YY. The diagram also shows two roads, one passing in front of the houses in Row-2 and another between the two blocks.
Some of the houses are occupied. The remaining ones are vacant and are the only ones available for sale.
The road adjacency value of a house is the number of its sides adjacent to a road. For example, the road adjacency values of C2, F2, and B1 are 2, 1, and 0, respectively. The neighbour count of a house is the number of sides of that house adjacent to occupied houses in the same block. For example, E1 and C1 can have the maximum possible neighbour counts of 3 and 2, respectively.
The base price of a vacant house is Rs. 10 lakhs if the house does not have a parking space, and Rs. 12 lakhs if it does. The quoted price (in lakhs of Rs.) of a vacant house is calculated as (base price) + 5 × (road adjacency value) + 3 × (neighbour count).
The following information is also known.
1. The maximum quoted price of a house in Block XX is Rs. 24 lakhs. The minimum quoted price of a house in block YY is Rs. 15 lakhs, and one such house is in Column-E.
2. Row-1 has two occupied houses, one in each block.
3. Both houses in Column-E are vacant. Each of Column-D and Column-F has at least one occupied house.
4. There is only one house with parking space in Block YY.
How many houses are vacant in Block XX?
Video Explanation

Which of the following houses are definitely occupied?
Video Explanation

Which of the following options best describes the number of vacant houses in Row-2?
Video Explanation

What is the maximum possible quoted price (in lakhs of Rs.) for a vacant house in Column-E?
Video Explanation

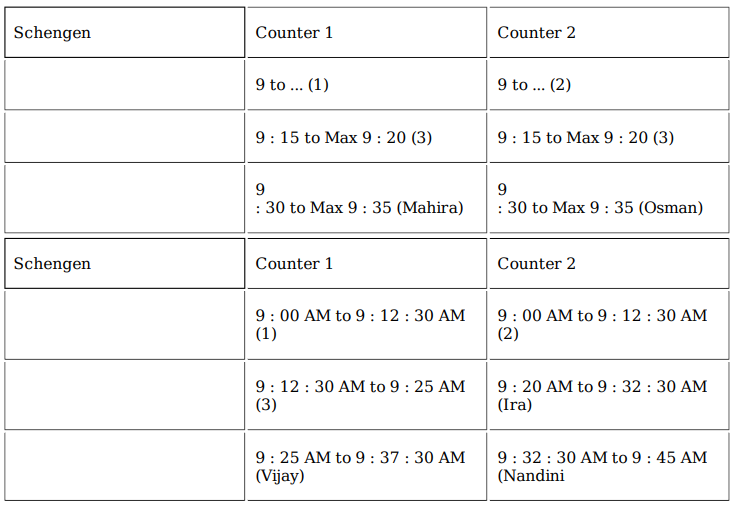
A visa processing office (VPO) accepts visa applications in four categories – US, UK, Schengen, and Others. The applications are scheduled for processing in twenty 15-minute slots starting at 9:00 am and ending at 2:00 pm. Ten applications are scheduled in each slot.
There are ten counters in the office, four dedicated to US applications, and two each for UK applications, Schengen applications and Others applications. Applicants are called in for processing sequentially on a first-come-first-served basis whenever a counter gets freed for their category. The processing time for an application is the same within each category. But it may vary across the categories. Each US and UK application requires 10 minutes of processing time. Depending on the number of applications in a category and time required to process an application for that category, it is possible that an applicant for a slot may be processed later.
On a particular day, Ira, Vijay and Nandini were scheduled for Schengen visa processing in that order. They had a 9:15 am slot but entered the VPO at 9:20 am. When they entered the office, exactly six out of the ten counters were either processing applications, or had finished processing one and ready to start processing the next.
Mahira and Osman were scheduled in the 9:30 am slot on that day for visa processing in the Others category.
The following additional information is known about that day.1. All slots were full.2. The number of US applications was the same in all the slots. The same was true for the other three categories.3. 50% of the applications were US applications.4. All applicants except Ira, Vijay and Nandini arrived on time.5. Vijay was called to a counter at 9:25 am.
How many UK applications were scheduled on that day?
Video Explanation

Which of the following is the closest to the time when Nandini's application process got over?
Video Explanation

When did the application processing for all US applicants get over on that day?
Video Explanation

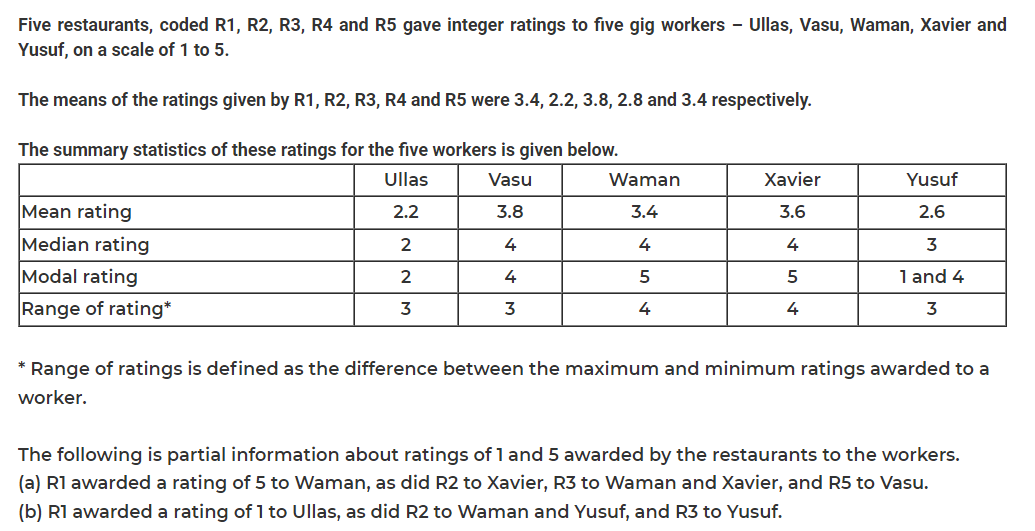
How many individual ratings cannot be determined from the above information?
Video Explanation

To how many workers did R2 give a rating of 4?
Video Explanation

What rating did R1 give to Xavier?
Video Explanation

What is the median of the ratings given by R3 to the five workers?
Video Explanation

Which among the following restaurants gave its median rating to exactly one of the workers?
Video Explanation

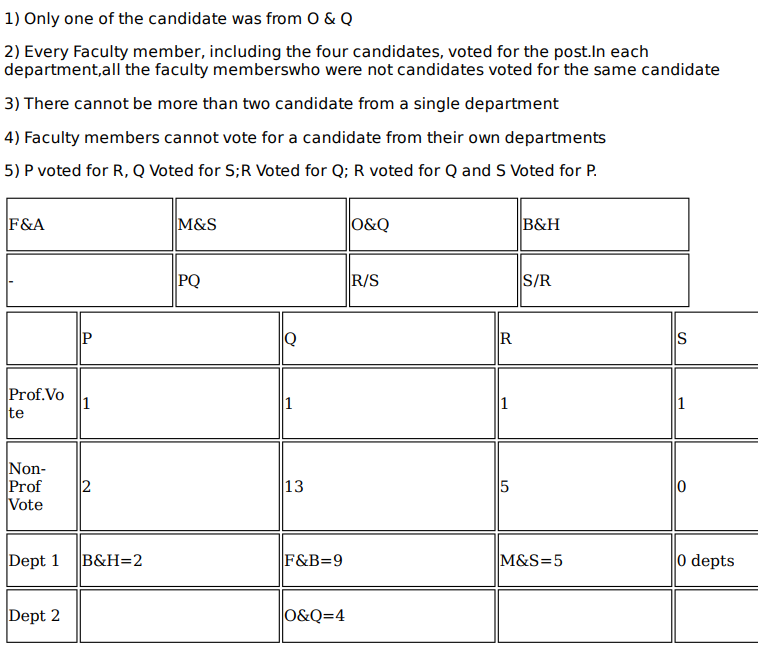
Faculty members in a management school can belong to one of four departments – Finance and Accounting (F&A), Marketing and Strategy (M&S), Operations and Quants (O&Q) and Behaviour and Human Resources (B&H). The numbers of faculty members in F&A, M&S, O&Q and B&H departments are 9, 7, 5 and 3 respectively.
Prof. Pakrasi, Prof. Qureshi, Prof. Ramaswamy and Prof. Samuel are four members of the school's faculty who were candidates for the post of the Dean of the school. Only one of the candidates was from O&Q.
Every faculty member, including the four candidates, voted for the post. In each department, all the faculty members who were not candidates voted for the same candidate. The rules for the election are listed below.
1. There cannot be more than two candidates from a single department.
2. A candidate cannot vote for himself/herself.
3. Faculty members cannot vote for a candidate from their own department.
After the election, it was observed that Prof. Pakrasi received 3 votes, Prof. Qureshi received 14 votes, Prof. Ramaswamy received 6 votes and Prof. Samuel received 1 vote. Prof. Pakrasi voted for Prof. Ramaswamy, Prof. Qureshi for Prof. Samuel, Prof. Ramaswamy for Prof. Qureshi and Prof. Samuel for Prof. Pakrasi.
Which two candidates can belong to the same department?
Video Explanation

Which of the following can be the number of votes that Prof. Qureshi received from a single department?
Video Explanation

If Prof. Samuel belongs to B&H, which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Prof. Pakrasi belongs to M&S.
Statement B: Prof. Ramaswamy belongs to O&Q.
Video Explanation

What best can be concluded about the candidate from O&Q?
Video Explanation

Which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Non-candidates from M&S voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Statement B: Non-candidates from F&A voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Video Explanation

A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle such that AB : CD = 2 : 1 and BC : AD = 5 : 4. If AC and BD intersect at the point E, then AE : CE equals
Video Explanation

In an examination, the average marks of 4 girls and 6 boys is 24. Each of the girls has the same marks while each of the boys has the same marks. If the marks of any girl is at most double the marks of any boy, but not less than the marks of any boy, then the number of possible distinct integer values of the total marks of 2 girls and 6 boys is
Video Explanation

Previous year papers
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018