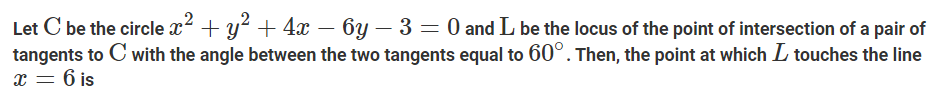Live Updates
• CATKing has launched new chat bot.

• New video on Logs has been released.
13.2K
Learners
asked the doubt

Previous Year Questions
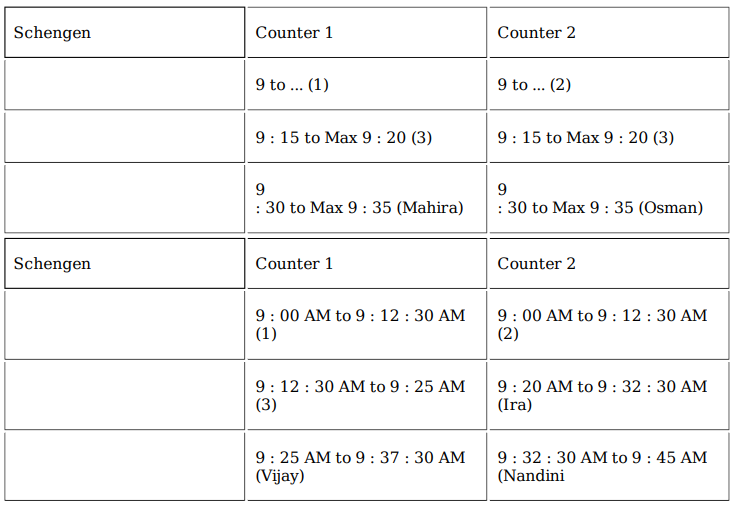
Which of the following is the closest to the time when Nandini's application process got over?
Video Explanation

When did the application processing for all US applicants get over on that day?
Video Explanation

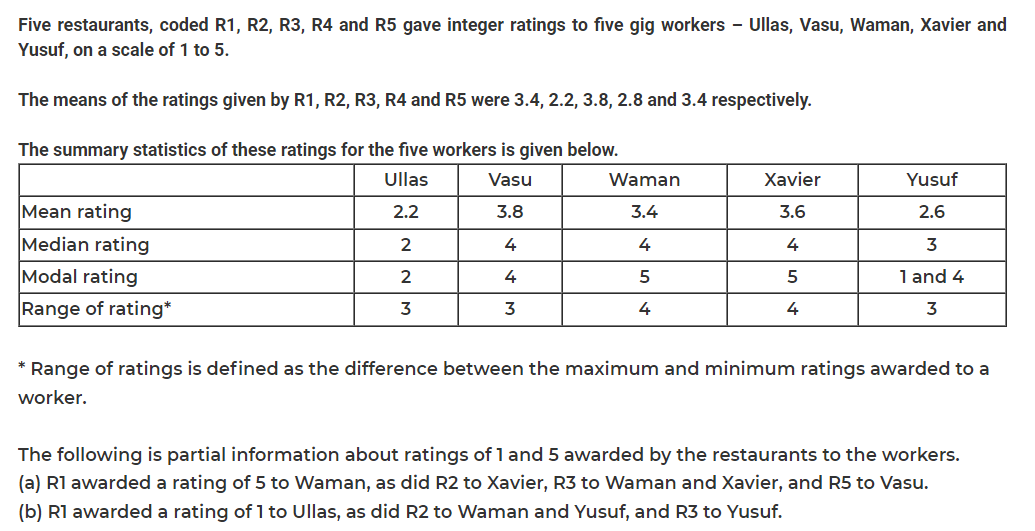
How many individual ratings cannot be determined from the above information?
Video Explanation

To how many workers did R2 give a rating of 4?
Video Explanation

What rating did R1 give to Xavier?
Video Explanation

What is the median of the ratings given by R3 to the five workers?
Video Explanation

Which among the following restaurants gave its median rating to exactly one of the workers?
Video Explanation

How many individual ratings cannot be determined from the above information?
Video Explanation

To how many workers did R2 give a rating of 4?
Video Explanation

What rating did R1 give to Xavier?
Video Explanation

What is the median of the ratings given by R3 to the five workers?
Video Explanation

Which among the following restaurants gave its median rating to exactly one of the workers?
Video Explanation

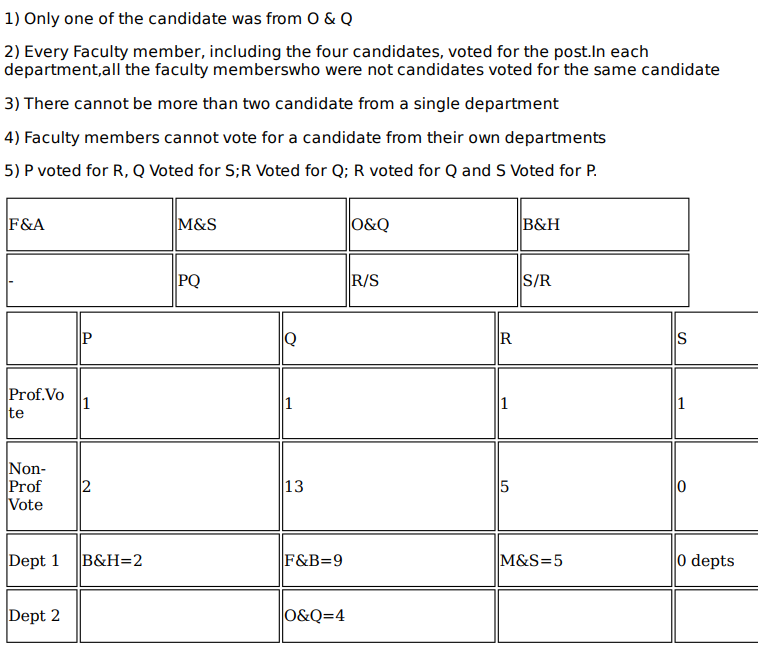
Faculty members in a management school can belong to one of four departments – Finance and Accounting (F&A), Marketing and Strategy (M&S), Operations and Quants (O&Q) and Behaviour and Human Resources (B&H). The numbers of faculty members in F&A, M&S, O&Q and B&H departments are 9, 7, 5 and 3 respectively.
Prof. Pakrasi, Prof. Qureshi, Prof. Ramaswamy and Prof. Samuel are four members of the school's faculty who were candidates for the post of the Dean of the school. Only one of the candidates was from O&Q.
Every faculty member, including the four candidates, voted for the post. In each department, all the faculty members who were not candidates voted for the same candidate. The rules for the election are listed below.
1. There cannot be more than two candidates from a single department.
2. A candidate cannot vote for himself/herself.
3. Faculty members cannot vote for a candidate from their own department.
After the election, it was observed that Prof. Pakrasi received 3 votes, Prof. Qureshi received 14 votes, Prof. Ramaswamy received 6 votes and Prof. Samuel received 1 vote. Prof. Pakrasi voted for Prof. Ramaswamy, Prof. Qureshi for Prof. Samuel, Prof. Ramaswamy for Prof. Qureshi and Prof. Samuel for Prof. Pakrasi.
Which two candidates can belong to the same department?
Video Explanation

Which of the following can be the number of votes that Prof. Qureshi received from a single department?
Video Explanation

If Prof. Samuel belongs to B&H, which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Prof. Pakrasi belongs to M&S.
Statement B: Prof. Ramaswamy belongs to O&Q.
Video Explanation

What best can be concluded about the candidate from O&Q?
Video Explanation

Which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Non-candidates from M&S voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Statement B: Non-candidates from F&A voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Video Explanation

Which two candidates can belong to the same department?
Video Explanation

Which of the following can be the number of votes that Prof. Qureshi received from a single department?
Video Explanation

If Prof. Samuel belongs to B&H, which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Prof. Pakrasi belongs to M&S.
Statement B: Prof. Ramaswamy belongs to O&Q.
Video Explanation

What best can be concluded about the candidate from O&Q?
Video Explanation

Which of the following statements is/are true?
Statement A: Non-candidates from M&S voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Statement B: Non-candidates from F&A voted for Prof. Qureshi.
Video Explanation

A quadrilateral ABCD is inscribed in a circle such that AB : CD = 2 : 1 and BC : AD = 5 : 4. If AC and BD intersect at the point E, then AE : CE equals
Video Explanation

In an examination, the average marks of 4 girls and 6 boys is 24. Each of the girls has the same marks while each of the boys has the same marks. If the marks of any girl is at most double the marks of any boy, but not less than the marks of any boy, then the number of possible distinct integer values of the total marks of 2 girls and 6 boys is
Video Explanation

The salaries of three friends Sita, Gita and Mita are initially in the ratio 5 : 6 : 7, respectively. In the first year, they get salary hikes of 20%, 25% and 20%, respectively. In the second year, Sita and Mita get salary hikes of 40% and 25%, respectively, and the salary of Gita becomes equal to the mean salary of the three friends. The salary hike of Gita in the second year is
Video Explanation

Let n be the least positive integer such that 168 is a factor of 1134n . If m is the least positive integer such that 1134n is a factor of 168m , then n+nm+m equals
Video Explanation

The minor angle between the hours hand and minutes hand of a clock was observed at 8:48 AM. The minimum duration, in minutes, after 8.48 am when this angle increases by 50% is
Video Explanation

Gita sells two objects A and B at the same price such that she makes a profit of 20% on object A and a loss of 10% on object B. If she increases the selling price such that objects A and B are still sold at an equal price and a profit of 10% is made on object B, then the profit made on object A will be nearest to
Video Explanation

A mixture P is formed by removing a certain amount of coffee from a coffee jar and replacing the same amount with cocoa powder. The same amount is again removed from mixture P and replaced with same amount of cocoa powder to form a new mixture Q. If the ratio of coffee and cocoa in the mixture Q is 16 : 9, then the ratio of cocoa in mixture P to that in mixture Q is
Video Explanation

The number of all natural numbers up to 1000 with non-repeating digits is
Video Explanation

Which one of the following cannot be inferred from Alexandra Schnell's experiment?
Video Explanation

The passage below is accompanied by a set of questions. Choose the best answer to each question.
Cuttlefish are full of personality, as behavioral ecologist Alexandra Schnell found out while researching the cephalopod's potential to display self-control. . . . "Self-control is thought to be the cornerstone of intelligence, as it is an important prerequisite for complex decision-making and planning for the future," says Schnell . . .
[Schnell's] study used a modified version of the "marshmallow test" . . . During the original marshmallow test, psychologist Walter Mischel presented children between age four and six with one marshmallow. He told them that if they waited 15 minutes and didn't eat it, he would give them a second marshmallow. A long-term follow-up study showed that the children who waited for the second marshmallow had more success later in life. . . . The cuttlefish version of the experiment looked a lot different. The researchers worked with six cuttlefish under nine months old and presented them with seafood instead of sweets. (Preliminary experiments showed that cuttlefishes' favorite food is live grass shrimp, while raw prawns are so-so and Asian shore crab is nearly unacceptable.) Since the researchers couldn't explain to the cuttlefish that they would need to wait for their shrimp, they trained them to recognize certain shapes that indicated when a food item would become available. The symbols were pasted on transparent drawers so that the cuttlefish could see the food that was stored inside. One drawer, labeled with a circle to mean "immediate," held raw king prawn. Another drawer, labeled with a triangle to mean "delayed," held live grass shrimp. During a control experiment, square labels meant "never."
"If their self-control is flexible and I hadn't just trained them to wait in any context, you would expect the cuttlefish to take the immediate reward [in the control], even if it's their second preference," says Schnell . . . and that's what they did. That showed the researchers that cuttlefish wouldn't reject the prawns if it was the only food available. In the experimental trials, the cuttlefish didn't jump on the prawns if the live grass shrimp were labeled with a triangle”many waited for the shrimp drawer to open up. Each time the cuttlefish showed it could wait, the researchers tacked another ten seconds on to the next round of waiting before releasing the shrimp. The longest that a cuttlefish waited was 130 seconds.
Schnell [says] that the cuttlefish usually sat at the bottom of the tank and looked at the two food items while they waited, but sometimes, they would turn away from the king prawn "as if to distract themselves from the temptation of the immediate reward." In past studies, humans, chimpanzees, parrots and dogs also tried to distract themselves while waiting for a reward.
Not every species can use self-control, but most of the animals that can share another trait in common: long, social lives. Cuttlefish, on the other hand, are solitary creatures that don't form relationships even with mates or young. . . . "We don't know if living in a social group is important for complex cognition unless we also show those abilities are lacking in less social species," says . . . comparative psychologist Jennifer Vonk.
All of the following constitute a point of difference between the "original" and "modified" versions of the marshmallow test EXCEPT that:
Video Explanation

Which one of the following, if true, would best complement the passage's findings?
Video Explanation

In which one of the following scenarios would the cuttlefish's behaviour demonstrate self-control?
Video Explanation

Which one of the following cannot be inferred from Alexandra Schnell's experiment?
Video Explanation

All of the following constitute a point of difference between the "original" and "modified" versions of the marshmallow test EXCEPT that:
Video Explanation

Which one of the following, if true, would best complement the passage's findings?
Video Explanation

In which one of the following scenarios would the cuttlefish's behaviour demonstrate self-control?
Video Explanation

All of the following arguments are made in the passage EXCEPT that:
Video Explanation

The passage below is accompanied by a set of questions. Choose the best answer to each question.
We cannot travel outside our neighbourhood without passports. We must wear the same plain clothes. We must exchange our houses every ten years. We cannot avoid labour. We all go to bed at the same time . . . We have religious freedom, but we cannot deny that the soul dies with the body, since 'but for the fear of punishment, they would have nothing but contempt for the laws and customs of society'. . . . In More's time, for much of the population, given the plenty and security on offer, such restraints would not have seemed overly unreasonable. For modern readers, however, Utopia appears to rely upon relentless transparency, the repression of variety, and the curtailment of privacy. Utopia provides security: but at what price? In both its external and internal relations, indeed, it seems perilously dystopian.
Such a conclusion might be fortified by examining selectively the tradition which follows More on these points. This often portrays societies where . . . 'it would be almost impossible for man to be depraved, or wicked'. . . . This is achieved both through institutions and mores, which underpin the common life. . . . The passions are regulated and inequalities of wealth and distinction are minimized. Needs, vanity, and emulation are restrained, often by prizing equality and holding riches in contempt. The desire for public power is curbed. Marriage and sexual intercourse are often controlled: in Tommaso Campanella's The City of the Sun (1623), the first great literary utopia after More's, relations are forbidden to men before the age of twenty-one and women before nineteen. Communal child-rearing is normal; for Campanella this commences at age two. Greater simplicity of life, 'living according to nature', is often a result: the desire for simplicity and purity are closely related. People become more alike in appearance, opinion, and outlook than they often have been. Unity, order, and homogeneity thus prevail at the cost of individuality and diversity. This model, as J. C. Davis demonstrates, dominated early modern utopianism. . . . And utopian homogeneity remains a familiar theme well into the twentieth century.
Given these considerations, it is not unreasonable to take as our starting point here the hypothesis that utopia and dystopia evidently share more in common than is often supposed. Indeed, they might be twins, the progeny of the same parents. Insofar as this proves to be the case, my linkage of both here will be uncomfortably close for some readers. Yet we should not mistake this argument for the assertion that all utopias are, or tend to produce, dystopias. Those who defend this proposition will find that their association here is not nearly close enough. For we have only to acknowledge the existence of thousands of successful intentional communities in which a cooperative ethos predominates and where harmony without coercion is the rule to set aside such an assertion. Here the individual's submersion in the group is consensual (though this concept is not unproblematic). It results not in enslavement but voluntary submission to group norms. Harmony is achieved without . . . harming others.
Following from the passage, which one of the following may be seen as a characteristic of a utopian society?
Video Explanation

Which sequence of words below best captures the narrative of the passage?
Video Explanation

All of the following statements can be inferred from the passage EXCEPT that:
Video Explanation

All of the following arguments are made in the passage EXCEPT that:
Video Explanation

Following from the passage, which one of the following may be seen as a characteristic of a utopian society?
Video Explanation

Which sequence of words below best captures the narrative of the passage?
Video Explanation

Previous year papers
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018